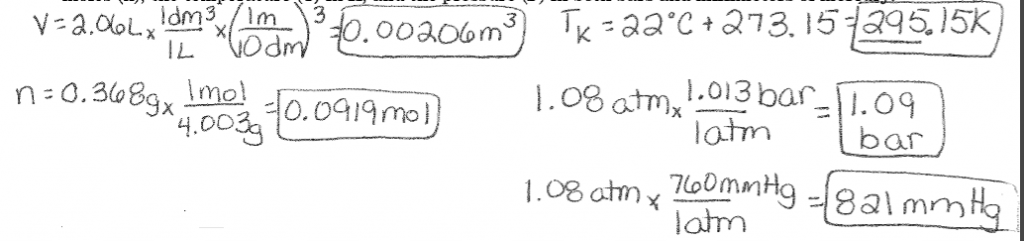The following abbreviations and units are commonly used:
V= Volume (usually in liters)
T = Temperature (always in Kelvin)
P = Pressure (usually in Pascals or atmospheres)
n= Amount (in moles)
The following unit conversions are useful to remember:
Volume conversion: 1L = 1000mL = 1000cm3 = 1dm3
Temperature conversion: TK = T°C + 273.15
Pressure conversion:
1atm= 760mmHg= 760 torr = 101.325kPa= 101,325 Pa = 14.7psi= 1.01325 bar
Mass conversion: mol= mass/molar mass
Standard conditions for Temperature and Pressure (STP):
Defined as P= 1atm, T= 273.15L, 1 mol of any gas occupies 22.4 L
Converting Units Example: A balloon with a volume (V) of 2.06L contains 0.368 g of Helium (MM= 4.003g/mol) at 22⁰C and 1.08 atm. Express the volume of the balloon in cubic meters, the amount of He in moles (n), the temperature (T) in K, and the pressure (P) in both bars and millimeters of mercury