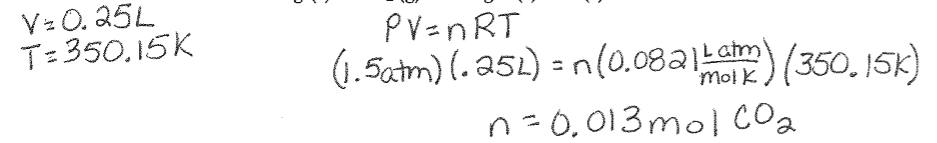Emil Clapeyron united all the gas laws mathematically into one ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
In the ideal gas law equation, R is the ideal gas constant. The value of R can vary depending on the unit used for pressure.
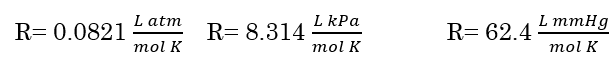
Ideal Gas Law Example: How much N2 is required to fill a small room with a volume of 960 cubic feet (27,000 L) to 745mm Hg at 25⁰C?
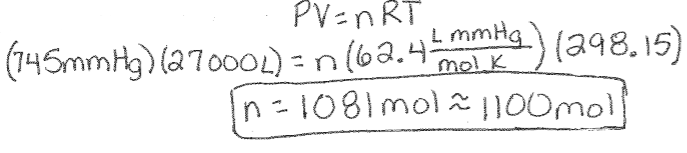
Ideal Gas Law Example: What is the volume that 500. g of iodine gas will occupy under the conditions: Temp = 300.oC and Pressure = 740. mm Hg?

Ideal Gas Law Example Using Stoichiometry: Find the volume of hydrogen gas produced when 38.2 g zinc reacts with excess hydrochloric acid at a pressure of 107.3 kPa and a temperature of 88°C.
Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) à ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
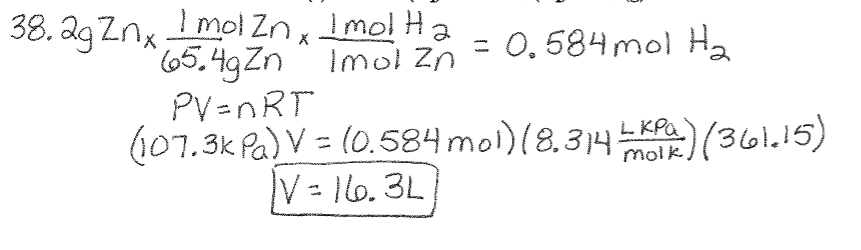
Ideal gas Law Example Using Stoichiometry: What mass of solid magnesium is required to reaction with 250 mL carbon dioxide at 1.5 atm and 77°C to produce solid magnesium oxide and solid carbon?
2Mg (s) + CO2 (g) à 2MgO (s) + C (s)